Mould temperature controllers (MTC) are essential devices in the manufacturing industry, particularly in processes such as injection molding, die casting, and extrusion. These systems are designed to precisely regulate the temperature of molds, ensuring the production of high-quality parts with consistent properties. By maintaining an optimal mold temperature, MTCs play a crucial role in improving production efficiency, reducing defects, and extending mold life.
A mould temperature controller functions through a closed-loop system that involves heating, cooling, and temperature monitoring. The device typically consists of a heating element, a cooling circuit, a pump, and a temperature control unit. Here's a breakdown of the key steps in its operation:
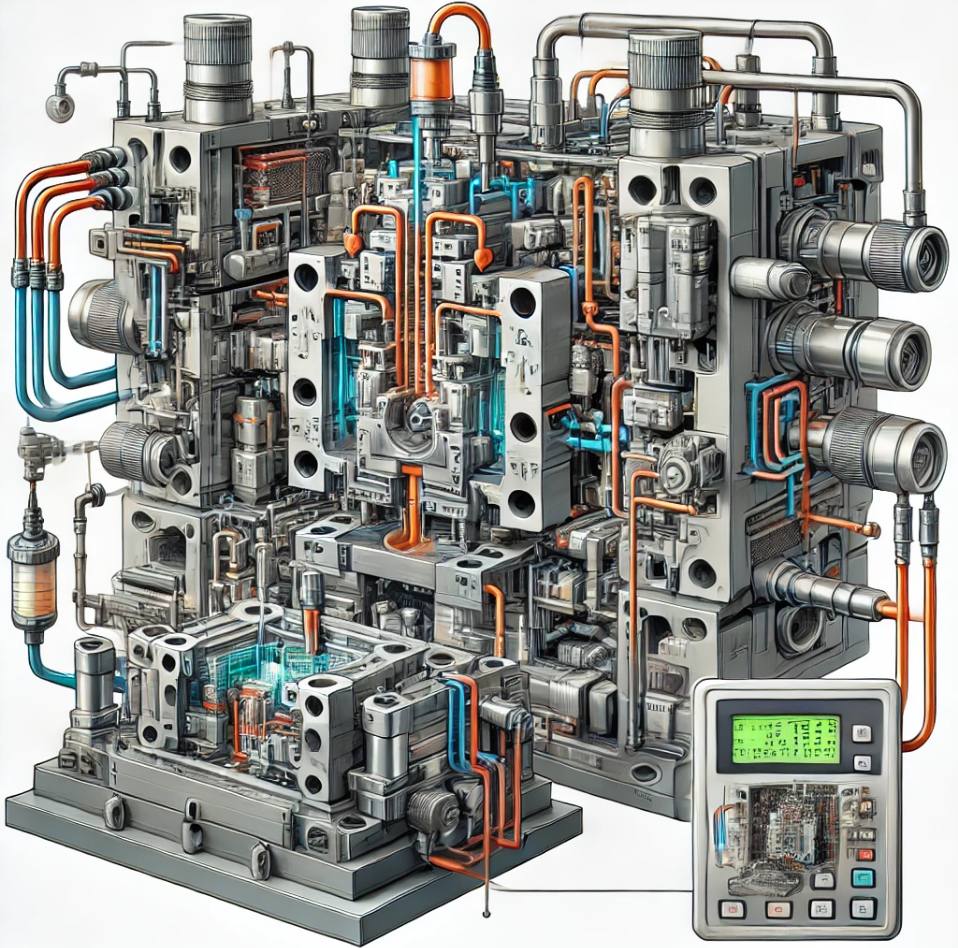
The MTC heats the mold to the desired temperature using an integrated heating element. This element is usually powered by electricity and controlled by a temperature sensor. The sensor monitors the mold’s surface temperature and sends real-time feedback to the controller. If the temperature falls below the set point, the heating element is activated to bring the mold back to the required level.
In some cases, excessive heat is generated during the manufacturing process, which can cause the mold temperature to exceed the optimal range. To counter this, the MTC uses a cooling circuit that circulates water or oil through channels within the mold. The coolant absorbs excess heat and transfers it away from the mold, helping maintain a stable temperature.
The core of an MTC’s operation is its closed-loop temperature control system. This system continuously monitors the mold’s temperature and adjusts heating or cooling accordingly. Advanced controllers use proportional-integral-derivative (PID) algorithms to ensure precise temperature regulation with minimal fluctuations.
MTCs are classified based on the type of fluid used for temperature control:
Water-based MTCs are commonly used for applications requiring temperatures up to 90-120°C. They are cost-effective, efficient, and suitable for molds that do not require extremely high temperatures. Water’s high thermal conductivity allows for rapid heat transfer, making these controllers ideal for processes with shorter cycle times.
Oil-based MTCs are used for applications requiring higher temperatures, typically ranging from 150°C to 350°C. Heat transfer oil has a higher boiling point than water, allowing it to maintain stability at elevated temperatures. These controllers are essential for materials and molds that demand precise temperature control in high-temperature environments.
Mould temperature controllers are utilized in various industries and manufacturing processes. Some common applications include:
In injection molding, maintaining a consistent mold temperature is critical to producing parts with uniform surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties. MTCs help minimize defects such as warping, shrinkage, and sink marks by ensuring optimal cooling and heating during the molding cycle.
Die casting involves injecting molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. Precise temperature control is essential to prevent defects such as cracks or porosity in the final product. MTCs ensure that the mold surface is neither too hot nor too cold, which could otherwise compromise the integrity of the casting.
In extrusion processes, maintaining a consistent temperature is crucial for achieving uniform material flow and dimensional stability. MTCs regulate the temperature of extrusion dies, ensuring smooth material extrusion and consistent product quality.
Rubber molding processes, such as compression and transfer molding, also benefit from precise temperature control. MTCs help optimize curing times and ensure consistent part quality by maintaining the required mold temperature throughout the process.
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet to its forming temperature and shaping it against a mold. MTCs ensure uniform heating and cooling of the mold, which is essential for achieving high-quality finished products.
Implementing an MTC in manufacturing processes offers numerous advantages:
Improved Product Quality: Consistent mold temperatures result in uniform parts with minimal defects.
Enhanced Production Efficiency: Reduced cycle times and minimized rework lead to higher productivity.
Extended Mold Life: Proper temperature regulation reduces thermal stress on the mold, prolonging its lifespan.
Energy Efficiency: Modern MTCs are designed to optimize energy consumption by balancing heating and cooling demands.
Process Stability: Precise temperature control reduces variability, leading to more predictable outcomes.
When selecting a mould temperature controller, it is essential to consider the following factors:
Temperature Range: Ensure the MTC can achieve the required temperature range for your specific application.
Heating and Cooling Capacity: The system’s capacity should align with the thermal demands of the mold.
Type of Heat Transfer Fluid: Choose between water or oil-based systems based on the temperature requirements.
Control Precision: Opt for controllers with advanced PID algorithms for accurate temperature regulation.
Build Quality and Reliability: Invest in high-quality MTCs from reputable manufacturers to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
Mould temperature controllers are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, enabling precise temperature regulation across a wide range of applications. By understanding their working principles, types, and applications, manufacturers can leverage these devices to improve product quality, enhance production efficiency, and reduce operational costs. Whether you’re involved in injection molding, die casting, or another temperature-sensitive process, an MTC is a valuable asset that ensures consistent and reliable results.

Copyright @2024 Pengqiang Intelligent Technology Group (Guangdong) Co., Ltd.
 Network Supported
Network Supported
