Industrial chillers play a crucial role in modern manufacturing and industrial processes by maintaining precise temperature control for various applications. This equipment is essential for industries such as plastics, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and chemicals, ensuring optimal efficiency and product quality. In this article, we will delve into the working principle of industrial chillers, explore their core components, and discuss their applications, all while addressing key questions relevant to industrial chiller manufacturers, OEMs, and end-users.
At its core, an industrial chiller is a refrigeration system designed to remove heat from a process or environment. The working principle is based on the vapor compression cycle or, in some cases, the absorption refrigeration cycle. Let’s break this down step by step:
The process begins with the chiller absorbing heat from the target area, such as industrial equipment, a manufacturing process, or a controlled environment. This is achieved through a heat exchanger, typically referred to as the evaporator. A circulating fluid, often water or a water-glycol mixture, absorbs the heat from the process and transfers it to the refrigerant within the evaporator.
The refrigerant, now in a low-pressure gaseous state, is compressed by the compressor. This step increases the refrigerant’s pressure and temperature, preparing it for heat rejection. Compressors used in industrial chillers can vary, including screw compressors, scroll compressors, or reciprocating compressors, depending on the application and cooling capacity required.
After compression, the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant enters the condenser. In the condenser, the refrigerant releases the absorbed heat to the external environment, often through air or water. Air-cooled chillers use fans to dissipate heat, while water-cooled chillers utilize a cooling tower or other water sources for heat rejection.
The refrigerant, now in a high-pressure liquid state, passes through an expansion valve. This step reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, turning it into a low-pressure liquid or vapor mixture. The refrigerant is then ready to re-enter the evaporator and repeat the cycle.
This continuous cycle ensures precise temperature control, making industrial chillers indispensable in many applications.
To understand the efficiency and reliability of industrial chillers, it is essential to know their main components:
Evaporator: Responsible for absorbing heat from the process fluid.
Compressor: Compresses the refrigerant and drives the refrigeration cycle.
Condenser: Releases heat from the refrigerant to the environment.
Expansion Valve: Controls the refrigerant flow and pressure.
Control System: Manages the operation of the chiller, ensuring stable performance.
Industrial chillers may also include additional components such as pumps, reservoirs, and advanced monitoring systems, depending on the specific design by the industrial chiller manufacturer or OEM.
Industrial chillers are broadly categorized into two types based on their cooling mechanism:
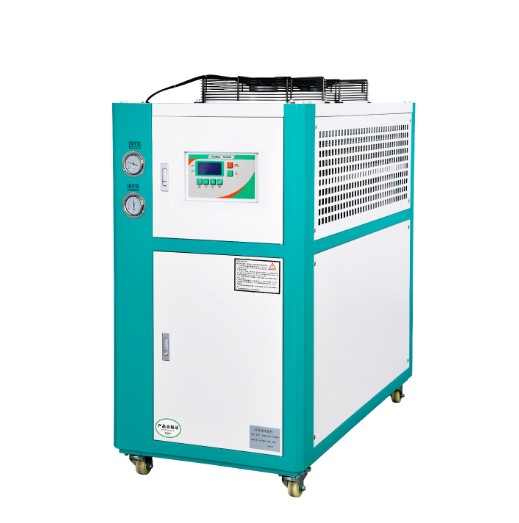

Air-cooled chillers use ambient air to dissipate heat through a condenser equipped with fans. These chillers are typically used in facilities with limited water access or where water conservation is a priority. They are easier to install and maintain but may have lower efficiency in high-temperature environments.
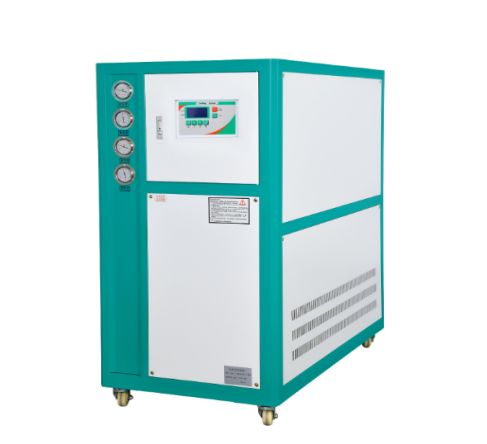

Water-cooled chillers rely on a cooling tower or external water source for heat rejection. They are more energy-efficient than air-cooled systems, especially in larger applications. However, they require a consistent water supply and more extensive maintenance.
Some manufacturers also offer hybrid chillers, combining the benefits of both air-cooled and water-cooled systems.
Industrial chillers are versatile and find applications across numerous industries. Here are some examples:
In plastic injection molding and extrusion, chillers maintain the temperature of molds and equipment, ensuring product consistency and reducing cycle times.
Precise temperature control is critical in pharmaceutical production and chemical processing. Industrial chillers help maintain stable conditions for reactors, fermenters, and storage tanks.
From cooling beverage tanks to preserving perishable food items, chillers are essential for maintaining hygiene and quality in food and beverage production.
Industrial chillers cool cutting fluids and machinery, preventing overheating and ensuring precision in machining processes.
Large-scale HVAC systems for commercial buildings often rely on industrial chillers for centralized cooling.
When selecting an industrial chiller, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance:
Cooling Capacity: Determine the heat load of your application and select a chiller with the appropriate cooling capacity.
Energy Efficiency: Look for chillers with high energy efficiency ratings to reduce operating costs.
Maintenance Requirements: Consider the maintenance demands of different chiller types.
Environmental Factors: Evaluate ambient conditions, water availability, and regulatory requirements.
Customization Options: Work with a reliable industrial chiller manufacturer or OEM to design a system tailored to your needs.
With advancements in technology, industrial chillers are becoming more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Here are some notable trends:
Smart Controls: Integration of IoT and AI for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: Transition to low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants to comply with environmental regulations.
Modular Designs: Flexible and scalable systems that can adapt to changing operational requirements.
Industrial chillers are essential for maintaining precise temperature control in various industrial and commercial applications. By understanding their working principles, components, and types, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting and operating these systems. Whether you’re a manufacturer, OEM, or end-user, investing in a high-quality industrial chiller from a trusted cold water machinery manufacturer ensures reliable performance and long-term cost savings.

Copyright @2024 Pengqiang Intelligent Technology Group (Guangdong) Co., Ltd.
 Network Supported
Network Supported
